ETF Investing in India 2025 | Benefits, Types & Best Platforms
Your Finances Team
Author

Ready to level up your money game without getting lost in boring finance talk?
If you're tired of seeing your savings sit in a bank account earning peanuts while inflation eats away at your purchasing power, ETFs might just be your ticket to financial freedom.
Think of ETFs as the Netflix of investing "“ you get access to a whole buffet of stocks and bonds for the price of one subscription. No cap, this could be the smartest financial move you make this year.
Whether you're saving for that dream bike, planning your first solo trip, or just want to flex on your friends with some serious investment knowledge, this guide will break down everything you need to know about ETF investing in India.
Let's dive in and make your money work as hard as you do on those weekend hustle projects!
What Are ETFs? Understanding Exchange Traded Funds
Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) are investment vehicles that track the performance of an index, commodity, bonds, or a basket of assets. Think of an ETF as a basket containing multiple stocks or bonds. When you buy shares of an ETF, you're essentially buying a small piece of this entire basket.
Unlike mutual funds, ETFs trade on stock exchanges like individual stocks. This means you can buy and sell ETF shares throughout trading hours at market prices. The beauty of ETFs lies in their simplicity "“ they offer instant diversification without requiring you to research and buy individual stocks.
ETFs in India have gained tremendous popularity among retail investors due to their low costs, transparency, and ease of trading. The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) regulates ETFs, ensuring investor protection and market integrity.
How ETFs Work in the Indian Market
ETFs operate on a unique structure that combines the best features of mutual funds and stocks. Here's how they function:
Creation and Redemption Process: Large institutional investors called Authorized Participants (APs) can create or redeem ETF shares directly with the fund company. This process helps keep the ETF's market price close to its Net Asset Value (NAV).
Tracking an Index: Most ETFs in India track popular indices like Nifty 50, Sensex, or sector-specific indices. The fund manager buys the same stocks in the same proportion as the index to replicate its performance.
Real-time Trading: Unlike mutual funds that price once daily, ETFs trade throughout market hours. You can see live prices and execute trades instantly through your trading account.
Transparency: ETF holdings are disclosed daily, allowing investors to see exactly what they own. This transparency helps in making informed investment decisions.
Types of ETFs Available in India
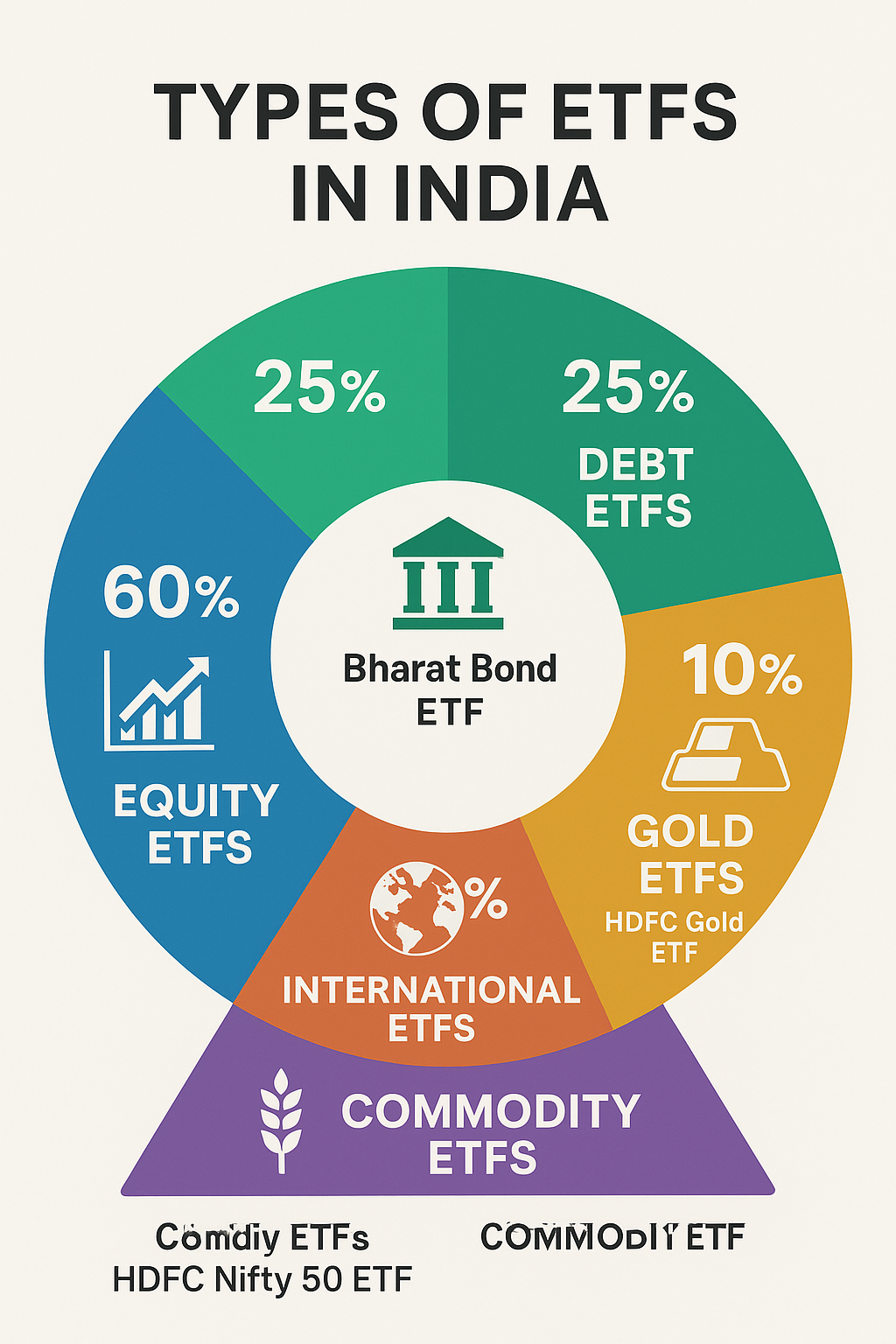
1. Equity ETFs
Broad Market ETFs: These track major indices like Nifty 50 or Sensex, providing exposure to the largest companies in India. Examples include HDFC Nifty 50 ETF and ICICI Prudential Sensex ETF.
Sectoral ETFs: Focus on specific sectors like banking, IT, or pharmaceuticals. Popular options include HDFC Bank ETF and ICICI Prudential Technology ETF.
Thematic ETFs: Target specific investment themes like ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) or dividend-paying companies.
Small Cap and Mid Cap ETFs: Provide exposure to smaller companies with higher growth potential but increased volatility.
2. Debt ETFs
Government Bond ETFs: Invest in government securities, offering stable returns with low risk. Examples include Bharat Bond ETF and CPSE Bond ETF.
Corporate Bond ETFs: Focus on high-quality corporate bonds, providing slightly higher returns than government bonds.
Liquid ETFs: Invest in short-term debt instruments, suitable for parking surplus funds temporarily.
3. Gold ETFs
Gold ETFs track the price of physical gold, allowing investors to gain exposure to gold without storing physical metal. Popular options include HDFC Gold ETF and ICICI Prudential Gold ETF.
4. International ETFs
These provide exposure to foreign markets, helping diversify beyond Indian borders. Examples include Motilal Oswal NASDAQ 100 ETF and ICICI Prudential US Bluechip Equity ETF.
5. Commodity ETFs
Apart from gold, India offers ETFs tracking other commodities, though options are limited compared to developed markets.
Benefits of ETF Investing in India
1. Low Cost Structure
ETFs typically have expense ratios ranging from 0.05% to 0.75%, significantly lower than actively managed mutual funds. This cost advantage compounds over time, resulting in higher net returns for investors.
2. Instant Diversification
A single ETF purchase gives you exposure to multiple securities. For example, buying a Nifty 50 ETF means you own a piece of India's top 50 companies across various sectors.
3. Transparency and Liquidity
ETF holdings are disclosed daily, and you can trade them during market hours. This liquidity makes ETFs suitable for both long-term investors and short-term traders.
4. Tax Efficiency
ETFs generally have lower portfolio turnover compared to actively managed funds, resulting in fewer taxable events and better after-tax returns.
5. Flexibility in Trading
You can buy ETFs in any quantity, unlike mutual funds that may have minimum investment requirements. Advanced trading strategies like stop-loss orders and limit orders are also possible.
6. No Lock-in Period
Unlike some mutual fund categories, ETFs have no lock-in period, providing complete liquidity flexibility.
How to Start Investing in ETFs in India

Step 1: Open a Demat and Trading Account
To invest in ETFs, you need:
- Demat Account: To hold your ETF shares electronically
- Trading Account: To buy and sell ETFs on the stock exchange
- Bank Account: Linked to your trading account for fund transfers
Popular brokers offering these services include Zerodha, Angel Broking, HDFC Securities, ICICI Direct, and Groww.
Step 2: Complete KYC Process
Submit required documents including:
- PAN card
- Aadhaar card
- Bank account details
- Photograph
- Income proof (for higher trading limits)
Step 3: Fund Your Account
Transfer money from your bank account to your trading account to start investing.
Step 4: Research and Select ETFs
Consider factors like:
- Expense ratio
- Tracking error
- Liquidity
- Assets under management (AUM)
- Underlying index performance
Step 5: Place Your Order
Use your broker's platform to:
- Search for the ETF by name or symbol
- Enter the number of shares you want to buy
- Choose order type (market or limit order)
- Execute the trade
Top ETF Investment Platforms in India
1. Zerodha Coin
- Zero commission on mutual fund investments
- User-friendly interface
- Comprehensive research tools
- Direct plan options available
2. Groww
- Simple mobile app interface
- No account opening charges
- Educational content for beginners
- SIP options for ETFs
3. HDFC Securities
- Established brand with strong research
- Multiple trading platforms
- Advisory services
- Regular market updates
4. ICICI Direct
- Comprehensive trading platform
- Research reports and recommendations
- Portfolio tracking tools
- Educational resources
5. Angel Broking (Angel One)
- Advanced charting tools
- Real-time market data
- Mobile trading app
- Customer support
Best ETFs to Consider in India (2025)
Large Cap Equity ETFs
- HDFC Nifty 50 ETF: Tracks Nifty 50 index with low expense ratio
- ICICI Prudential Sensex ETF: Follows BSE Sensex performance
- UTI Nifty ETF: One of the oldest and most liquid ETFs
Sectoral ETFs
- HDFC Bank ETF: Exposure to banking sector
- ICICI Prudential Technology ETF: IT sector focus
- Nippon India Pharma ETF: Pharmaceutical sector exposure
Gold ETFs
- HDFC Gold ETF: High liquidity and low tracking error
- ICICI Prudential Gold ETF: Competitive expense ratio
- Axis Gold ETF: Strong fund house backing
International ETFs
- Motilal Oswal NASDAQ 100 ETF: US technology exposure
- ICICI Prudential US Bluechip Equity ETF: Diversified US market exposure
Debt ETFs
- Bharat Bond ETF: Government-backed bond ETF
- CPSE Bond ETF: Central Public Sector Enterprise bonds
ETF Investment Strategies for Indian Investors
1. Core-Satellite Strategy
Use broad market ETFs (like Nifty 50 ETF) as your core holding (70-80% of portfolio) and add sectoral or thematic ETFs as satellites (20-30%) for additional returns.
2. Systematic Investment Plan (SIP)
Invest a fixed amount regularly in ETFs to benefit from rupee cost averaging. While not all brokers offer direct SIP in ETFs, you can manually invest fixed amounts monthly.
3. Dollar Cost Averaging
Buy ETFs at regular intervals regardless of market conditions to average out the purchase price over time.
4. Asset Allocation Strategy
Combine different types of ETFs:
- 60% Equity ETFs for growth
- 30% Debt ETFs for stability
- 10% Gold ETFs for inflation protection
5. Rebalancing
Review and rebalance your ETF portfolio periodically to maintain desired asset allocation.
Tax Implications of ETF Investing in India
Equity ETFs
- Short-term capital gains (holding period < 1 year): Taxed at 15%
- Long-term capital gains (holding period ≥ 1 year): Taxed at 10% on gains exceeding ₹1 lakh per year
Debt ETFs
- Short-term capital gains (holding period < 3 years): Added to income and taxed as per tax slab
- Long-term capital gains (holding period ≥ 3 years): Taxed at 20% with indexation benefit
Gold ETFs
- Short-term capital gains (holding period < 3 years): Added to income and taxed as per tax slab
- Long-term capital gains (holding period ≥ 3 years): Taxed at 20% with indexation benefit
International ETFs
- Similar to debt ETFs taxation
- Additional considerations for foreign tax credit
Risks Associated with ETF Investing
1. Market Risk
ETFs are subject to market volatility. If the underlying index falls, the ETF value will also decline.
2. Tracking Error
ETFs may not perfectly replicate index performance due to fees, cash holdings, and timing differences.
3. Liquidity Risk
Some ETFs may have low trading volumes, making it difficult to buy or sell at desired prices.
4. Concentration Risk
Sectoral ETFs may be heavily concentrated in few stocks, increasing risk.
5. Currency Risk
International ETFs expose investors to currency fluctuations between rupee and foreign currencies.
6. Counterparty Risk
Synthetic ETFs using derivatives face counterparty risk from the derivative provider.
ETF vs Mutual Funds: Making the Right Choice
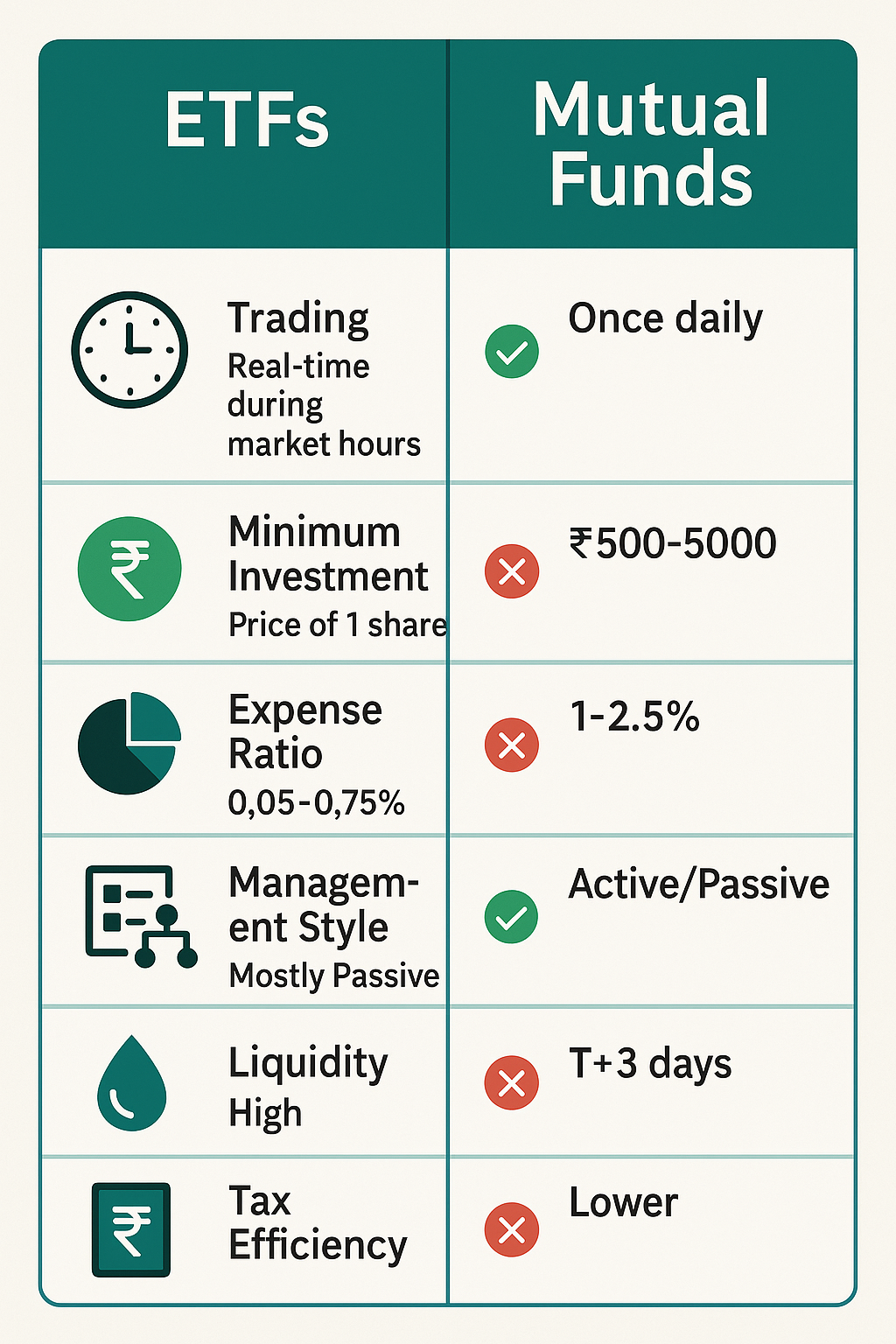
Cost Comparison
ETFs generally have lower expense ratios (0.05%-0.75%) compared to actively managed mutual funds (1%-2.5%).
Trading Flexibility
ETFs can be traded during market hours, while mutual funds price only once daily.
Investment Amount
ETFs can be bought for the price of one share, while mutual funds may have minimum investment requirements.
Professional Management
Mutual funds offer active management, while most ETFs follow passive strategies.
Dividend Handling
ETFs typically distribute dividends, while mutual funds often reinvest them automatically.
Building Your First ETF Portfolio
For Beginners (Conservative Approach)
- 40% Nifty 50 ETF
- 30% Debt ETF
- 20% Gold ETF
- 10% International ETF
For Moderate Risk Takers
- 50% Large Cap ETF
- 20% Mid Cap ETF
- 15% Sectoral ETF
- 10% Gold ETF
- 5% International ETF
For Aggressive Investors
- 40% Large Cap ETF
- 25% Mid Cap ETF
- 20% Sectoral ETFs
- 10% International ETF
- 5% Gold ETF
Future of ETF Investing in India
The ETF market in India is rapidly evolving with several trends shaping its future:
1. Product Innovation
Expect more thematic ETFs focusing on emerging trends like artificial intelligence, renewable energy, and digital transformation.
2. Increased Adoption
Growing investor awareness and simplified investment processes will drive ETF adoption among retail investors.
3. Regulatory Support
SEBI continues to introduce investor-friendly regulations to promote ETF growth and protect investor interests.
4. Technology Integration
Improved trading platforms and mobile apps will make ETF investing more accessible to younger investors.
5. International Expansion
More international ETFs will provide Indian investors access to global markets and currencies.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in ETF Investing
1. Overtrading
ETFs are best suited for long-term investing. Frequent trading can erode returns through transaction costs.
2. Ignoring Expense Ratios
Small differences in expense ratios compound significantly over time. Always compare costs before investing.
3. Lack of Diversification
Don't put all money in one type of ETF. Diversify across asset classes and geographies.
4. Market Timing
Trying to time the market often leads to poor returns. Stick to systematic investing approaches.
5. Not Understanding the Underlying Index
Know what your ETF tracks and understand the index methodology before investing.
6. Ignoring Liquidity
Choose ETFs with good trading volumes to ensure easy entry and exit.
ETF Investment Tips for Success
1. Start Early
Begin investing as soon as possible to benefit from compound growth over time.
2. Stay Informed
Regularly review your ETF holdings and stay updated on market trends and economic developments.
3. Keep It Simple
Start with broad market ETFs before moving to sectoral or thematic options.
4. Regular Review
Conduct quarterly reviews of your portfolio and rebalance if necessary.
5. Emergency Fund First
Ensure you have 6-12 months of expenses in emergency funds before investing in ETFs.
6. Goal-based Investing
Align your ETF investments with specific financial goals and time horizons.
Technology and ETF Investing
Mobile Trading Apps
Modern broking apps make ETF investing convenient with features like:
- Real-time quotes
- One-click trading
- Portfolio tracking
- Research reports
- Educational content
Robo-advisors
AI-powered platforms are beginning to offer ETF-based portfolio management, making professional investment advice accessible to retail investors.
Data Analytics
Advanced analytics help investors track performance, analyze costs, and optimize portfolios using ETFs.
ETF Investment for Different Life Stages
Students and Young Professionals (20-30 years)
- Focus on equity ETFs for maximum growth
- Start small but invest consistently
- Take advantage of long investment horizon
Mid-career Professionals (30-50 years)
- Balanced approach with equity and debt ETFs
- Increase investment amounts as income grows
- Focus on specific goals like children's education
Pre-retirement (50-60 years)
- Gradually shift to conservative ETFs
- Maintain some equity exposure for inflation protection
- Focus on capital preservation
Post-retirement (60+ years)
- Emphasize debt and dividend ETFs
- Maintain small equity allocation
- Focus on regular income generation
Conclusion
ETF investing in India offers an excellent opportunity for wealth creation through diversified, low-cost, and transparent investment vehicles. Whether you're a beginner looking to start your investment journey or an experienced investor seeking to optimize your portfolio, ETFs provide the flexibility and efficiency needed to achieve your financial goals.
The key to successful ETF investing lies in understanding your risk tolerance, investment objectives, and time horizon. Start with broad market ETFs, gradually diversify across asset classes, and maintain a long-term perspective. With proper research, disciplined investing, and regular portfolio review, ETFs can become a cornerstone of your wealth-building strategy.
Remember, while ETFs offer numerous advantages, they're not without risks. Always consult with financial advisors if needed and never invest more than you can afford to lose. The journey to financial freedom through ETF investing requires patience, discipline, and continuous learning.
As the Indian financial markets continue to evolve and mature, ETFs will likely play an increasingly important role in democratizing investing and helping millions of Indians build wealth for their future. Start your ETF investment journey today and take the first step toward achieving your financial dreams.
Written by
Your Finances Team
Helping Indians make better financial decisions through simple, actionable advice.
Continue Reading

9 Essential Money Checkpoints Every Indian Should Complete Before Turning 40
Turning 40 is crucial for financial planning; complete 9 essential checkpoints to secure a rich, fulfilling life in India....

12 Common Mutual Fund Mistakes That Are Costing Indian Investors Crores (And How to Avoid Them)
Let's be real — investing in mutual funds isn't rocket science, but somehow many of us still mess it up big time. Whether you're a college student starting your first SIP with ₹500 or someone who ...
Best Gold ETFs in 2025: Complete Guide for Indian Investors
Gold has always been a precious metal highly valued in Indian culture, traditionally bought for weddings, festivals, and as a store of wealth. However, the way Indians invest in gold has evolved signi...